Competitive sports demand physical excellence and pose various challenges to athletes. One significant obstacle they often face is shoulder injuries. Being highly involved in most athletic activities, the shoulders are vulnerable to a range of injuries that can impede an athlete’s performance and potentially end their careers. In this article, we will explore the common shoulder injuries athletes encounter, their causes, and practical strategies for prevention and recovery.
The Anatomy of the Shoulder: Understanding Vulnerabilities
Before delving into the types of injuries, it is crucial to grasp the complex anatomy of the shoulder joint. The shoulder comprises the humerus (upper arm bone), scapula (shoulder blade), and clavicle (collarbone). This joint’s remarkable mobility allows for a wide range of movements, making it susceptible to various injuries.
Common Shoulder Injuries in Competitive Sports
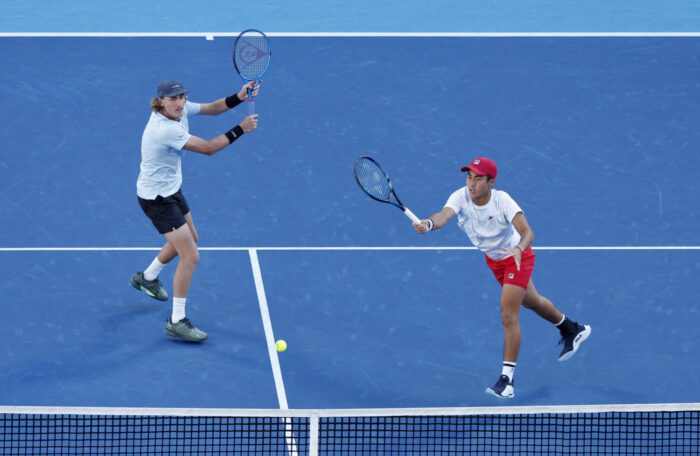

Source: sportsinjurybulletin.com
- Rotator Cuff Tears: The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that stabilize the shoulder joint. Repetitive motions and overuse can lead to tears in these tendons, causing pain, weakness, and limited range of motion. Athletes involved in sports like baseball, tennis, and swimming often experience rotator cuff tears.
- Shoulder Dislocations: A shoulder dislocation occurs when the humerus pops out of its socket. This injury can happen due to trauma, such as a hard fall or direct impact. Athletes in contact sports like football, rugby, and wrestling are more prone to shoulder dislocations.
- Labral Tears: The labrum is a ring of cartilage that surrounds the shoulder socket, enhancing stability. Athletes involved in overhead activities like volleyball or weightlifting risk developing labral tears. Symptoms include pain, clicking sensations, and a feeling of shoulder instability.
- Shoulder Impingement: Shoulder impingement syndrome occurs when the tendons of the rotator cuff become irritated or inflamed. Athletes engaging in repetitive overhead motions, such as throwing or serving, are susceptible to this condition. Symptoms include pain during movement, weakness, and difficulty lifting objects overhead.
Reference: https://primalphysicaltherapy.com/most-common-shoulder-injuries-in-sports/
Causes of Shoulder Injuries
Source: gleneagles.com.sg
- Overuse and Repetitive Motions: The constant repetition of specific movements in sports can place excessive strain on the shoulder joint and surrounding tissues, leading to injuries over time. Athletes performing throwing, serving, or overhead movements are prone to overuse injuries.
- Trauma and Direct Impact: Collisions, falls, or direct blows to the shoulder can cause acute injuries like dislocations, fractures, or ligament sprains. Contact sports like football, hockey, and martial arts carry a higher risk of traumatic shoulder injuries.
- Muscle Imbalances and Weakness: Athletes who neglect proper strength training and conditioning may develop muscle imbalances and weaknesses. These imbalances can affect shoulder stability and increase the risk of injuries.
Prevention and Recovery Strategies

Source: avantortho.com.sg
- Proper Conditioning and Training: Athletes should prioritize comprehensive strength and conditioning programs that target the shoulder muscles and promote overall balance and stability. Specific exercises to strengthen the rotator cuff, scapular stabilizers, and core muscles can help prevent shoulder injuries.
- Warm-up and Stretching: Athletes should warm up adequately to increase blood flow and loosen up the shoulder joints and muscles before engaging in any athletic activity. Dynamic stretching exercises that target the shoulder complex can enhance flexibility and reduce the risk of injury.
- Technique and Form: Proper technique and form are vital in sports to minimize shoulder stress. Athletes should receive coaching and guidance on correct movement patterns and mechanics specific to their sport. This includes learning how to land safely, throw with proper mechanics, and execute overhead movements with precision.
- Rest and Recovery: Adequate rest and recovery are essential for injury prevention. Athletes should incorporate rest days into their training schedules to allow their bodies to recover and repair. Additionally, getting sufficient sleep, maintaining a balanced diet, and managing stress are crucial for overall shoulder health.
- Gradual Progression and Cross-Training: Gradually increasing the intensity, duration, or frequency of training can help the body adapt and minimize the risk of overuse injuries. Incorporating cross-training activities that vary the stress placed on the shoulders can also reduce the likelihood of repetitive strain injuries.
- Proper Equipment and Gear: Athletes should use appropriate protective equipment and gear designed for their sport. This may include shoulder braces, supportive straps, or padding to provide additional stability and reduce the risk of impact-related injuries.
Rehabilitation and Treatment
Source: flintrehab.com
Proper rehabilitation is crucial for a successful recovery in the unfortunate event of a shoulder injury. Treatment options may vary depending on the type and severity of the injury but often include:
- Physical Therapy: A tailored physical therapy program can help restore shoulder strength, flexibility, and range of motion. Therapists may incorporate exercises, manual therapy techniques, and modalities like heat or ice to promote healing and recovery.
- Medication: In some cases, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or pain-relieving medications may be prescribed to manage pain and reduce inflammation.
- Surgical Intervention: Severe cases of shoulder injuries, such as large tears or recurrent dislocations, may require surgical intervention. Surgery aims to repair damaged structures, stabilize joints, and restore proper function.
- Post-surgery Rehabilitation: Following surgery, a comprehensive rehabilitation program will be prescribed to regain strength, mobility, and function gradually. This typically involves a combination of physical therapy, exercises, and close monitoring by healthcare professionals.
Conclusion
Shoulder injuries pose a significant hurdle for athletes in competitive sports. Understanding the common types of injuries and their causes and implementing effective prevention strategies are vital for athletes to stay in the game and maintain optimal performance.
By prioritizing proper conditioning, technique, and recovery, athletes can minimize the risk of shoulder injuries and ensure a triumphant return to their sport after injury. Always consult a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation and personalized advice for your situation. Stay strong, stay safe, and protect those shoulders!
